How do CNC Machining Center work?
Machining centres are versatile, automated machine tools. They enable a variety of complex machining operations to be carried out with great precision. Whether drilling, milling or turning, these machines are used in many industrial sectors.
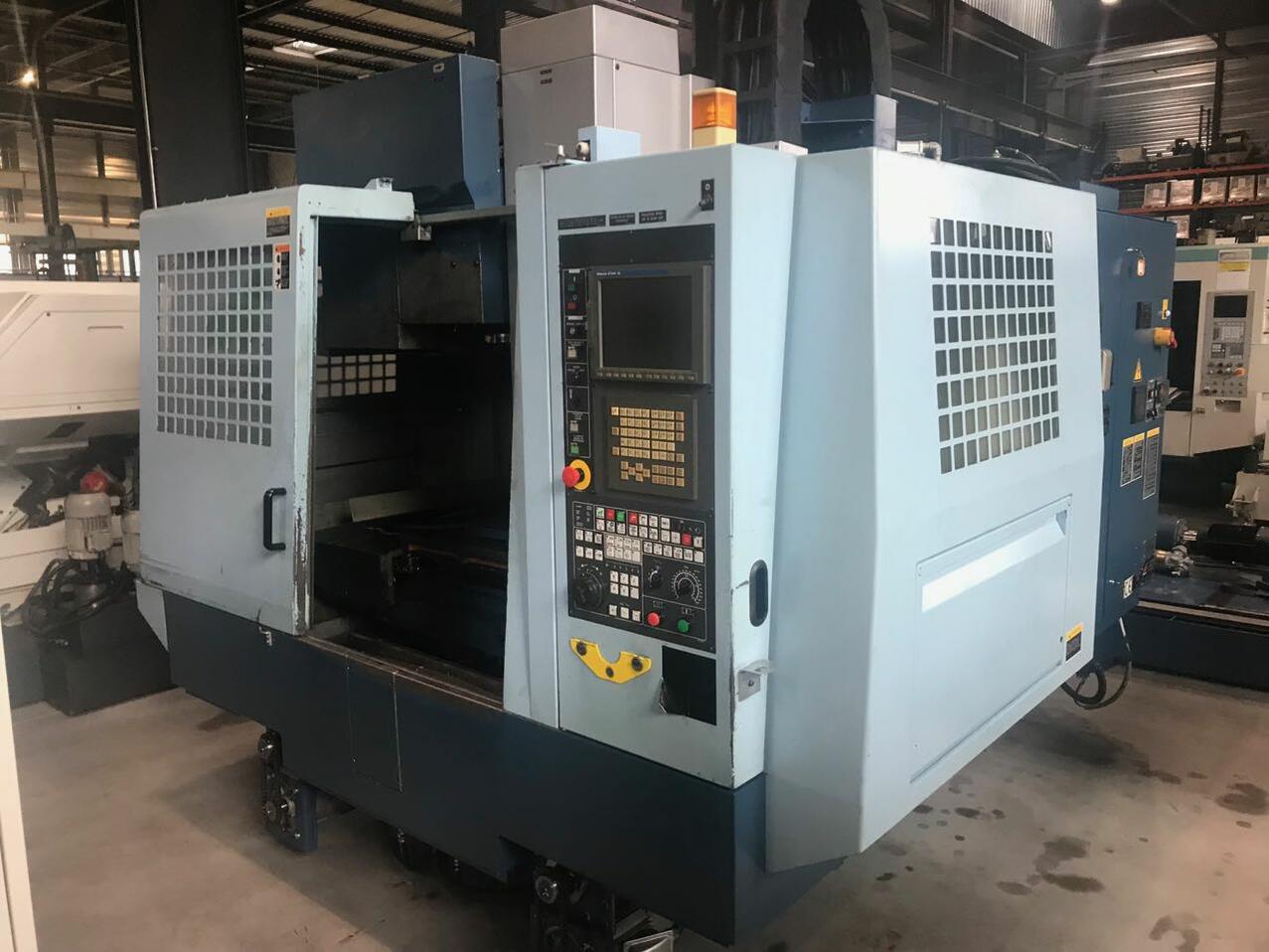
Vertical CNC machining centres are most commonly used because they are accessible and easy to program. They are suitable for small production runs or operations requiring frequent tool changes. They also provide good visibility of the machining area. Operators can therefore monitor the precision of the machining without hindrance.
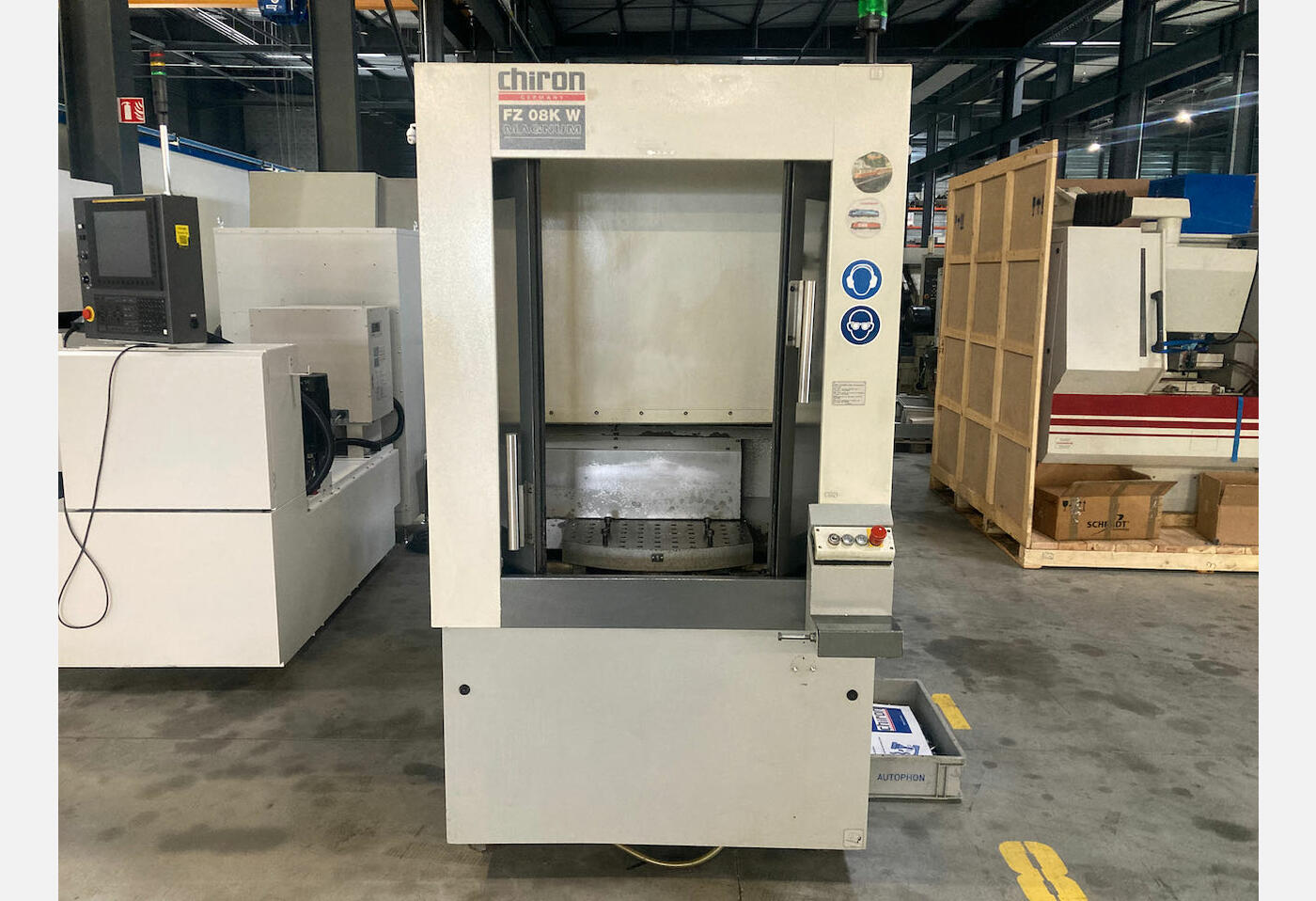
Vertical machining centres (CNC) are among the most common. As their name suggests, the spindle, which holds and rotates the cutting tool, is oriented vertically. This configuration is well suited to work on flat workpieces, such as surface milling or drilling.

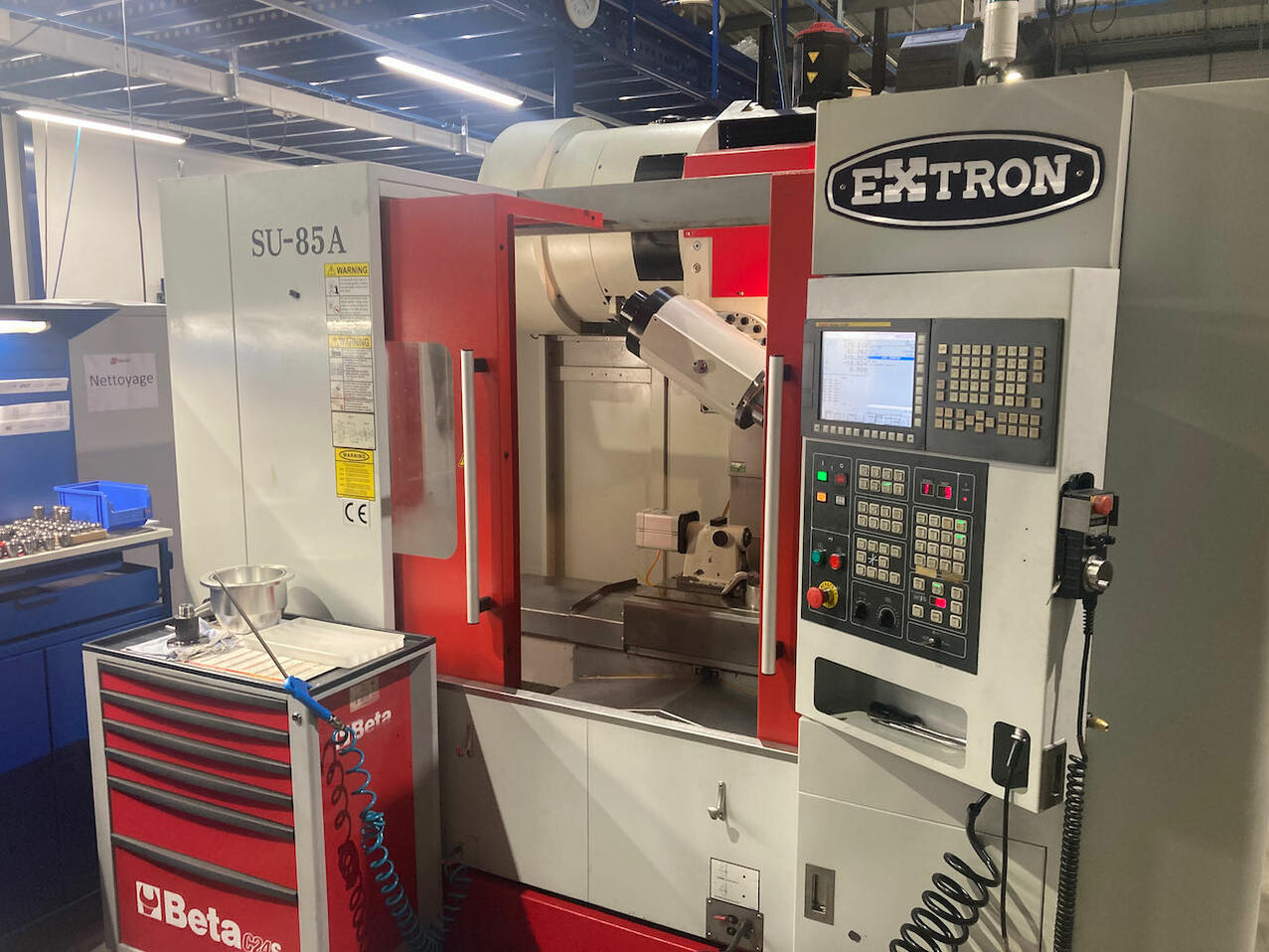
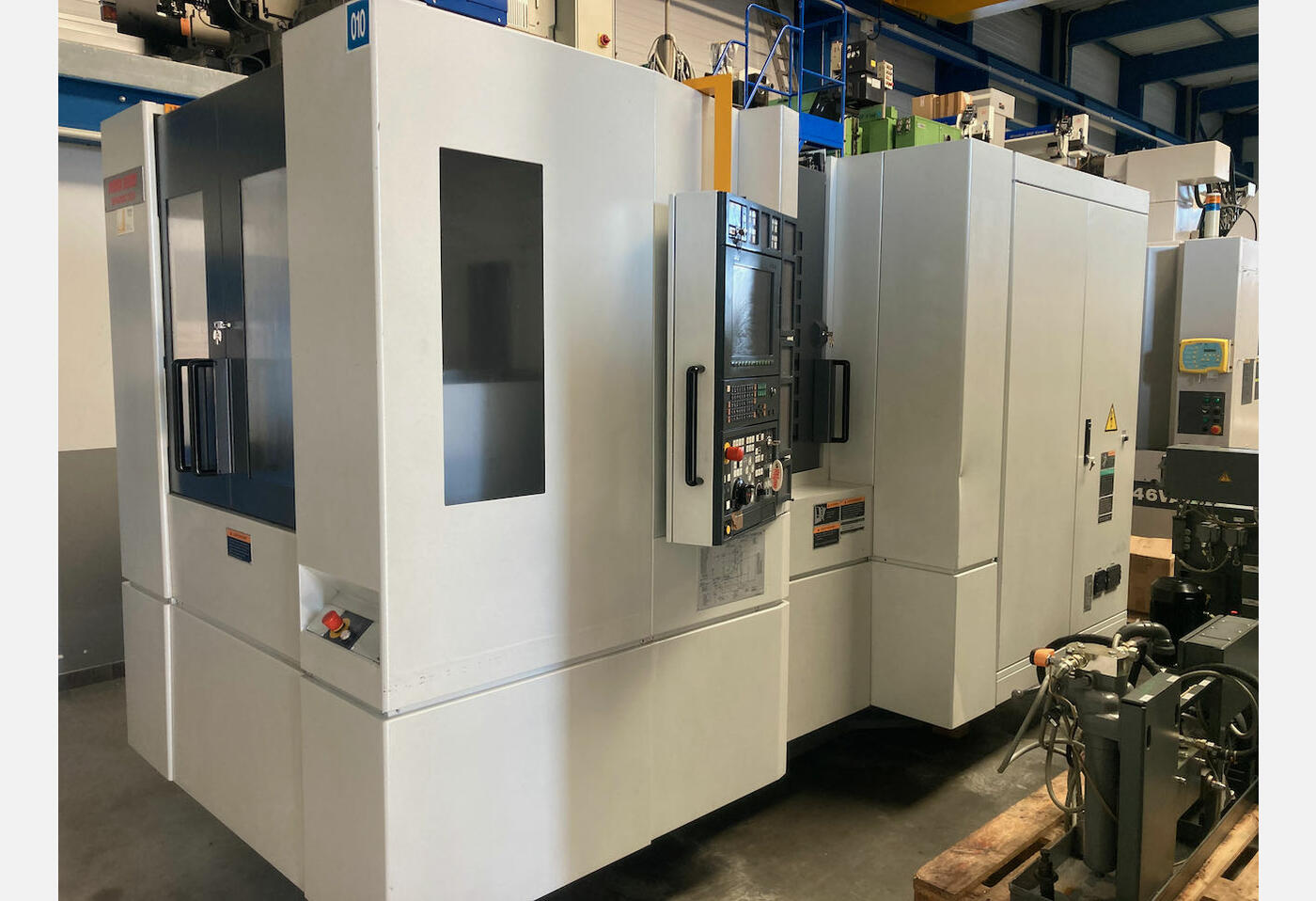
Unlike vertical machining centres, horizontal machining centres have a horizontally oriented spindle. This type of machine is used for jobs where a lot of material needs to be removed. Thanks to gravity, the chips fall naturally out of the work area.
A horizontal machining centre is often used for more complex parts. With this type of machine tool, machining can be carried out on several sides. These machines reduce workpiece handling time. This is because they often have rotating tables. This mobility allows the operator to process several sides of a part without manual repositioning. As a result, companies save time on mass production, which is carried out with great efficiency. The same applies to the processing of bulky materials that require high precision.

The precision and flexibility of machining centres depend largely on the number of axes available. See a diagram of the axes on a machining centre.
The more axes a machine has, the more complex it will be able to perform operations without having to reposition the part with its hands.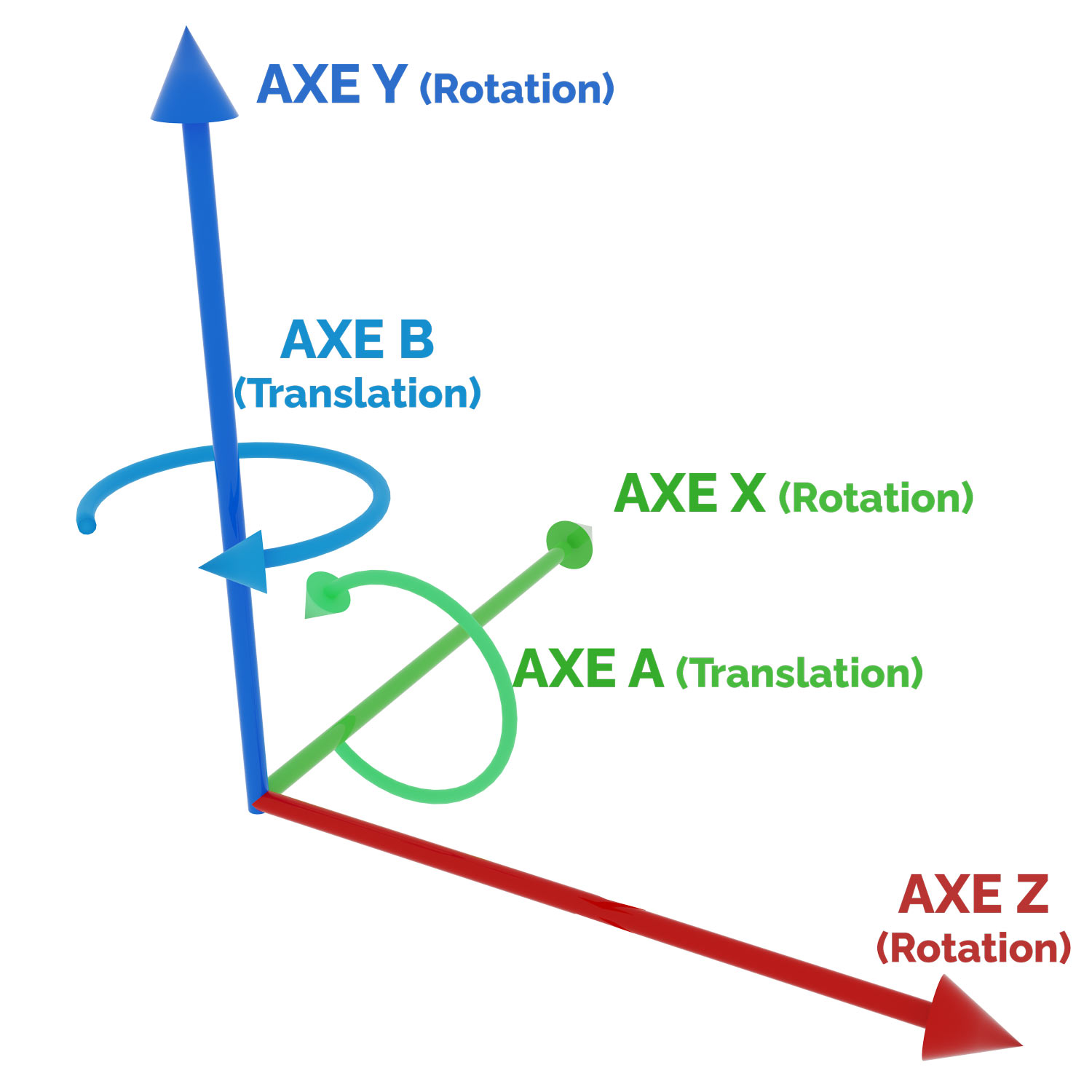
Vertical and horizontal machining centres are widely used tools in the manufacturing industry. Their ability to machine with precision and automate processes improves production efficiency. 3-, 4- and 5-axis centres meet the specific requirements of each project.
Looking for a used machine tool? See also our guide to the different types of grinding machines.
Vertical machining centres
Vertical CNC machining centres are most commonly used because they are accessible and easy to program. They are suitable for small production runs or operations requiring frequent tool changes. They also provide good visibility of the machining area. Operators can therefore monitor the precision of the machining without hindrance.
Vertical machining centres (CNC) are among the most common. As their name suggests, the spindle, which holds and rotates the cutting tool, is oriented vertically. This configuration is well suited to work on flat workpieces, such as surface milling or drilling.

Horizontal machining centres
Unlike vertical machining centres, horizontal machining centres have a horizontally oriented spindle. This type of machine is used for jobs where a lot of material needs to be removed. Thanks to gravity, the chips fall naturally out of the work area.
A horizontal machining centre is often used for more complex parts. With this type of machine tool, machining can be carried out on several sides. These machines reduce workpiece handling time. This is because they often have rotating tables. This mobility allows the operator to process several sides of a part without manual repositioning. As a result, companies save time on mass production, which is carried out with great efficiency. The same applies to the processing of bulky materials that require high precision.

How the axes of a machining centre work
The precision and flexibility of machining centres depend largely on the number of axes available. See a diagram of the axes on a machining centre.
The more axes a machine has, the more complex it will be able to perform operations without having to reposition the part with its hands.

3-axis machining centre
A 3-axis machining centre is capable of moving in the X, Y and Z directions. These movements drive drilling, milling of flat surfaces and cutting. The 3-axis machining centre is limited to relatively simple parts, as it cannot access all the faces of a part without repositioning.4-axis machining centre
A 4-axis machining centre works like a traditional CNC machine with 3 linear axes (X, Y and Z). The only difference is that it adds a 4th axis, called the A axis, which rotates around the X axis. This rotation machines parts on several sides without having to remove them from the machine. Accuracy is improved and production time is reduced. In a single operation, the part is machined from all sides.5-axis machining centre
5-axis machining centres offer ultimate flexibility. They perform simultaneous movements on 5 axes (X, Y, Z, A and B) to machine complex parts without repositioning. This CNC machine tool is ideal for irregular shapes. It reduces handling errors and improves finishing. It is used in the aerospace, automotive and medical industries for parts requiring high precision.Vertical and horizontal machining centres are widely used tools in the manufacturing industry. Their ability to machine with precision and automate processes improves production efficiency. 3-, 4- and 5-axis centres meet the specific requirements of each project.
Looking for a used machine tool? See also our guide to the different types of grinding machines.



